The skin is the largest organ of the body. The importance of your skin and its place on your body cannot be overstated. Not only does it act as a protective layer for all your other organs and structures, but it also plays a role in your daily life, from breathing to excreting to telling or giving you what's going on in your body. It is the speaker of your health, so human skin is the outer shell of the body. In humans, it is the largest organ of nutrition - as it interacts with the environment, the skin plays an important immune role in protecting the body from pathogens and excessive water loss.
What is skin used for? Skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area and weight. The skin consists of two layers: dermis and dermis. Beneath the dermis is the hypodermis or subcutaneous fat. The skin has three main functions: protection, regulation and sensitivity. The skin performs vital functions to maintain the physiological and biochemical conditions of the body in an optimal state.
The most important functions of the skin are: • Regulation of body temperature. • Prevention of loss of body fluids and entry of toxic substances. • Protect the body from the harmful effects of the sun and radiation. Toxic substances are excreted in sweat. Mechanical support. Immune function is controlled by Langerhans cells. Sensory system of touch, heat, cold and social sensations - sexual and emotional. Vitamin D content. Precursors exposed to sunlight and internal steroids.
SKIN FUNCTION - DEFENSE: The first line of defense against the external environment, the skin is constantly renewing itself and removing tens of thousands of dead cells every minute to protect the body: Mechanical shocks: The skin behaves as before. Barrier to withstand any pressure, strain or impact. If this mechanical impact is stronger than the skin, the injury takes the form of a skin tear, which causes the skin to lose one or more functions. Our skin helps retain the fluids and moisture our body needs and protects us from absorbing foreign fluids or fluids. We can shower, swim and walk in the rain without worry. Our skin prevents the absorption of any harmful substances or the loss of excess water from the skin. Promotes movement and growth: growth of body and body tissues and conditioning of body skin during movement. Radiation: Although it does not affect the skin, the ultraviolet (UV) rays emitted by the sun will damage the tissues beneath our body. This protection is provided by the melanin pigmentation of the epidermis. The skin and its pigmentation protect us from many diseases such as skin cancer, but as it does not provide complete protection, excessive sun exposure should be avoided by using sunscreen and appropriate clothing. . The skin is covered by a thin, moist, oily layer that prevents most substances or organisms (such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi) from entering the skin. The epidermis also contains Langerhans cells that help regulate the immune response to pathogens that come into contact with the skin. Thermoregulation: The skin helps regulate temperature through sweat glands and blood vessels in the dermis. Increased evaporation of secreted sweat lowers body temperature. Vasodilation (relaxation of small blood vessels) of the dermis facilitates the release of heat from the body and the lowering of body temperature through the skin. During vasoconstriction (narrowing of small blood vessels), the dermis maintains a certain internal body temperature. The subcutaneous fat layer also acts as an insulating barrier, preventing body heat loss and helping to reduce the effects of cold temperatures. Sensation: One of the most important functions of the dermis of the skin is to detect various sensations of heat, cold, pressure, contact and pain. Sensation is determined by easily damaged nerve endings located in the dermis. This feeling on the skin acts as a protection against burns. Skin sensation can protect us from first and second degree burns, but in third degree burns it is less effective because we do not feel pain due to the destruction of nerve endings in the skin. (Indicates a more serious injury). Endocrine function: the skin is one of the main sources of vitamin D due to the production of cholecalciferol (D3) in the two lower layers of the epidermis.
The main role of the skin is as follows: The skin plays an important role in protecting our body: 1. Fights external irritation, 2. Regulates body temperature, 3. Prevents loss of blood and body fluids. That's why it's so important to keep our skin looking its best.
Skin Health: The health of your skin is not only important for your appearance, but also because your skin plays many important roles for your body. Your skin protects your body from the many viruses and bacteria you encounter every day. It also protects you from the sun's rays, especially UV rays that can damage cells. Healthy skin produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, and vitamin D is essential for many bodily functions. Healthy skin helps your body maintain a constant temperature. Healthy skin helps you better respond to important changes in your environment, such as pain or pressure. Signs and symptoms: 1. Signs of inflammation (redness, heat, swelling, pain and fever) 2. Signs of infection (itching, fever, swelling and pain) 3. Allergic reaction (itching, redness, hives or rash, heat) 4 Skin moles Abnormalities (irregular, large, painful or itchy) 5. New nodules, lumps or skin discoloration.
Skin care Avoid excessive sun exposure (use sunscreen, sunscreen, and protective clothing) Wash regularly with soap and water. Facial moles, skin wrinkles, sweaty areas (legs, underarms or between layers) • Apply to skin - Moisturizing recipe (to prevent dryness and cracking) - Avoid walking barefoot.
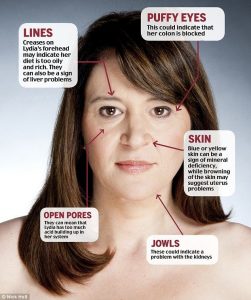
What Your Skin Says About Your Health Your skin is the largest organ in your body, so changes in your hair, skin, or nails can be a sign that something is going on under the skin. While problem skin may mean you need to change your beauty routine, your skin condition could be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. It's time to dig deeper. Chronically dry skin is usually caused by two things: eczema and general dryness or weather. Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin disease, can cause the skin to become dry, itchy, inflamed, and cracked. asthma and hay fever. - Acne on chin and chin Have you got acne on your chin and chin again? A jump in these areas can indicate a possible hormonal imbalance. This type of adult acne is very common in women who did not have acne during their teenage years. But don't worry, otherwise the problem of hormonal acne can increase in women. It can increase during stress or menstruation. Menopause Unusual hair growth: Unwanted hair growth in traditionally male areas, such as around the chin or below the navel, can be a sign of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). It plays a role in hair growth. If you're concerned about other symptoms of PCOS, such as an inability to lose weight despite diet and exercise or irregular periods, see your doctor to rule out PCOS. This could be the cause of your cycle. Dark eyes can be a combination of genetics, age or lifestyle. Anatomically, the fat and structural support around the eyes changes with age, so you may see more holes. Dark skin under the eyes can also be caused by lack of nutrition, hydration or sleep. Sunspots - Freckles and dark spots are a measure of a lifetime of sun damage. Most sun damage occurs during childhood and adolescence and can increase the risk of skin cancer. Check your skin for any changes, such as moles, bumps, or sores that won't heal. Dry, dull skin can make your skin look dull and dull. Dry winter weather can also affect pale skin. Drinking enough water and getting enough sleep can improve the appearance of your skin. "Red doesn't mean all red bumps are acne-like lesions, and gray skin, redness, and dry skin can be symptoms of rosacea. This chronic skin condition is caused by environmental and genetic factors, spicy foods, exercise, and stress. — Irritated eyelids Eyes swelling can be allergic If the irritation is accompanied by a rash, you may have eczema (a common symptom in adults is dryness and a rash on the eyelids) or I see contact dermatitis from the irritating product.eyelid dermatitis Or people should look at all the products they use, from the applicator to the makeup. Chronic redness on the forehead and cheeks can be dilated blood vessels due to chronic rosacea. Severe redness can also occur. Women due to hormonal changes, for example, menopause. also see a doctor.Your veins is an important indicator of healthy blood circulation. Usage Spider veins or varicose veins in the legs indicate deeper bleeding due to age, weight and genetics and may indicate future health problems. The cause of venus on the face can be excessive stress or rosacea. Dark spots: Dark pigmentation on the face in women (commonly known as melasma) is hormonal and often associated with pregnancy. Although not indicative of an underlying medical problem, it can be the result of hormonal fluctuations and can be made worse by sun exposure. A red, red rash is usually caused by contact dermatitis, which means the skin comes into contact with something irritating and the skin has an immune response. But a rash on warm, moist skin can also be caused by a fungal infection, which is common in people with untreated diabetes. Your mind and body may be showing something called alopecia areata. This autoimmune disease often has a genetic component and can occur in healthy people. Sudden and sudden hair loss, called telogen shedding, is usually caused by things like childbirth, severe emotional stress, high fever, infection, or serious illness, but it usually grows back within three months. The gateway to your health. If you have discoloration, dark spots, or a change in the shape of your nails or toenails, these could be signs of internal problems under the skin, from vitamin deficiencies to liver disease. If it does not heal, it may indicate a bleeding disorder. However, as you age, your body also bruises more easily because as your skin thins, the capillaries move closer to the surface. Medications such as blood thinners can also cause bruising, but consult your doctor if you experience severe bruising or new bruising after starting treatment. This may indicate a possible skin infection. Other causes of slow healing include skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma), blood clotting disorders, or diabetes. People with undiagnosed diabetes may see black spots on the front of their feet. Known as diabetic dermatopathy, this may be a sign that you need to see your doctor for further tests. Food is important for health. An unhealthy diet can disrupt metabolism, cause weight gain, and even affect organs such as the heart and liver. What you eat also affects the health of another organ: your skin. As we learn more about how diet affects the body, it's becoming increasingly clear that what you eat can have a huge impact on the health and aging of your skin.
Here are some foods that improve skin health: Oily fish. Oily fish like salmon, mackerel and herring are great for skin health. ...Lawyer. Avocados are high in healthy fats. ... nut. ...Sunflower seeds. …Sweet potatoes. ... red or yellow pepper. … broccoli. ... Tomato.